Project AbstractCover crops are an ever-growing trend throughout Prairie Canada, but little is known about the benefits and detrimental effects of their addition to crop rotations on our fields. This project will evaluate the viability, impact, and benefits of including cover crops in crop rotations across Prairie Canada (including MB, SK, and AB) over the four-year period. By the end of this project, we hope to get more information on the potential for adoption of a range of cover crops across different growing environments in the prairies, along with their agronomic, environmental, and economic benefits and drawbacks. |
|
||||||||||
Project Objectives
|
|||||||
Methods |
||||||||||||
|
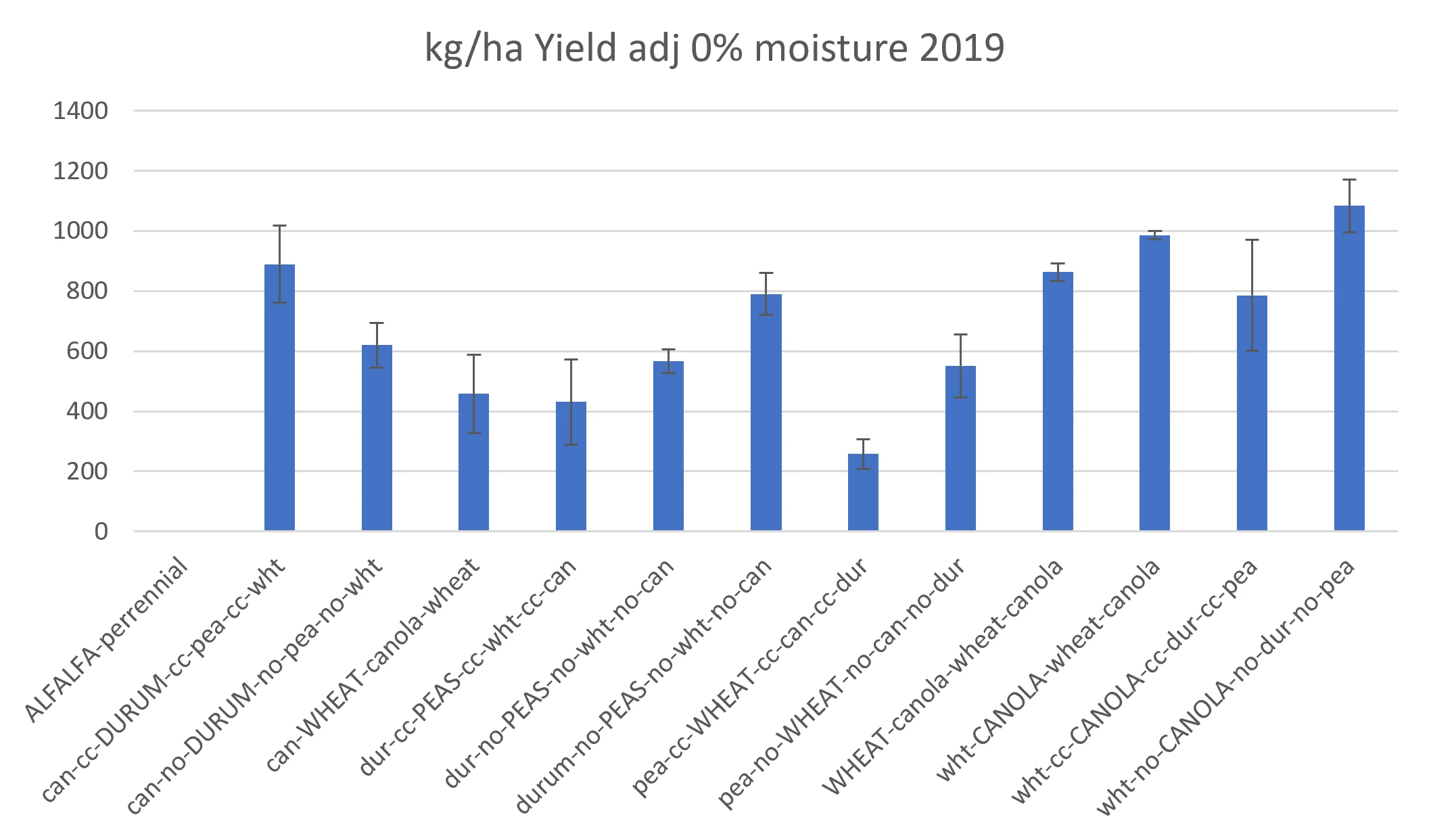
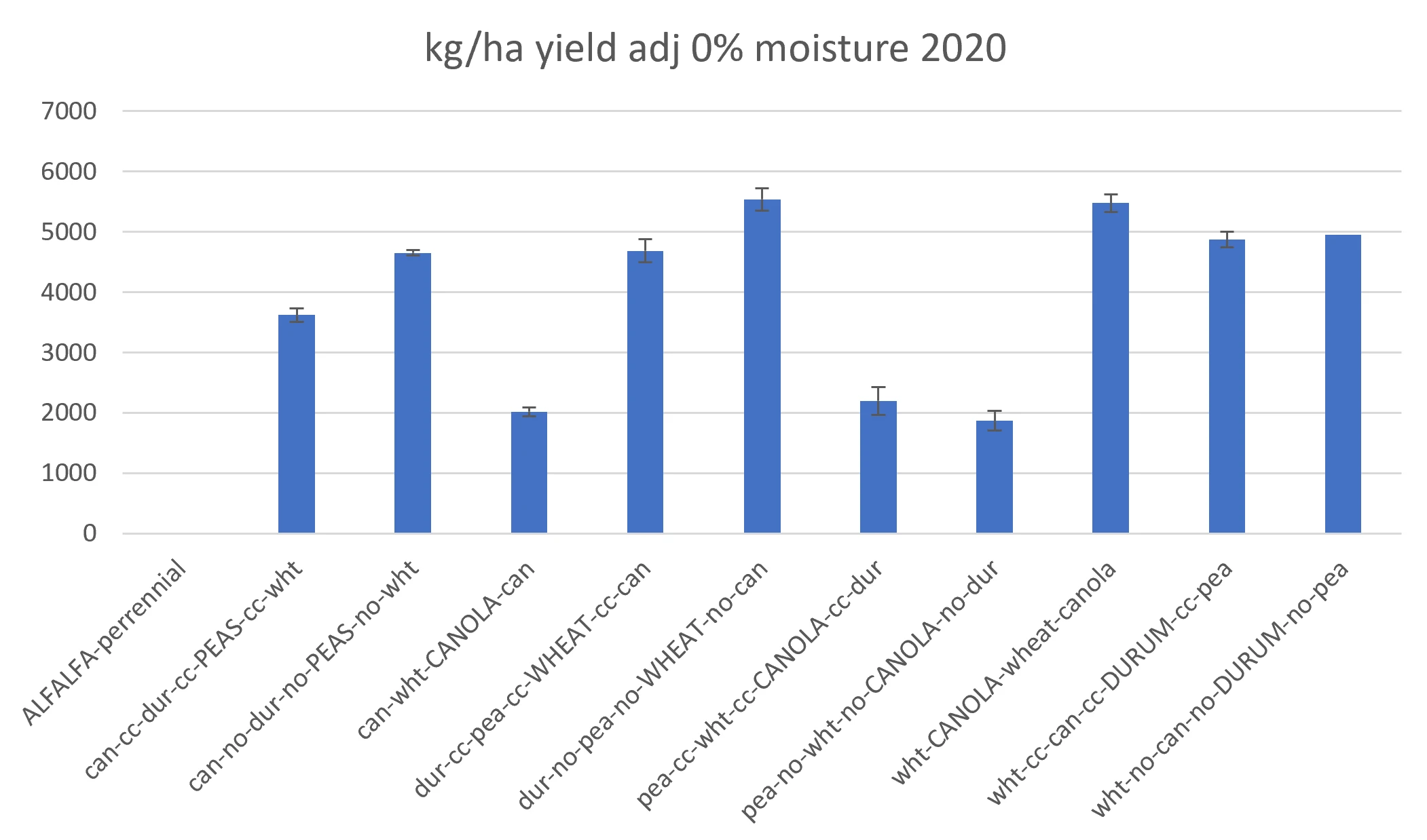
Lethbridge crop rotation will be wheat, canola, durum, and then pea. |
|||||||||||
Grain CropsTillage system: Reduced tillage systems. Use tillage when required to incorporate crop or cover crop residue to create a good seedbed. Use direct seeding or reduce tillage where possible or representative of standard practices in your growing area. You will need to use your experience and judgement. Seeding: Select a representative variety and seeding rate for each crop type for your growing area, to allow for more timely cover crop seeding ≥ consider selecting a variety on the early side for your area. Select an appropriate seeder for each crop. Disc drills are important if direct seeding into cover crop residue Fertilizer: Fertilizer rates for each crop type will be based on fall soil test and local lab recommendations. Select a representative target yields for your research farm/growing area for each crop. Fertilizer rates should be the same for treatments with and without cover crops. Although soil tests will be conducted by plot (by rep in year 1), select one rate for each crop and apply to all plots with that crop in the experiment for that growing season. Herbicides: Apply pre-plant and in-crop herbicides as required for adequate grassy and broadleaf weed control. Use label rates. Be mindful of spray drift to neighboring plots for both cash and cover crops. Other mechanical and cultural control practices can be used in combination with herbicides based on your experience and judgment. Fungicides and insecticides: fungicides and insecticides should be applied as seed treatment or sprayed in-crop following standard practice for your growing area. When possible, disease and insect damage should be limited so that they do not mask rotation differences. Harvesting: Harvest each crop in the rotation at the appropriate time with the appropriate equipment. Identify a representative area that is one plot combine pass within each plot that will have minimal sampling disturbance during the growing season to quantify grain yield. Sub-samples of grains will be saved each year of the study. Perennial Crop CheckEstablish an alfalfa or alfalfa-grass forage mix that is adapted to your growing area in year 1 of the experiment. This perennial treatment is a check treatment for soil quality measurements in the final years of the study. The perennial crops should be hayed (or cut and raked off) at least once per year. The cut forage must be removed from the plot area. The perennial crops should be fertilized annually based on soil test recommendations or standard practice in your growing area. If the stand is poor ≥ inter-seed in the spring or fall to fill in the stand. Control weeds as required.
ResultsSign in or subscribe to view. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
ResultsPreliminary Results.
There is still a lot of data to be analyzed for this project with regard to the perennial check, soil health, carbon sequestration and GHG emissions. The final report will relay that information as much of it is from other site locations. |
|||||||||||||||
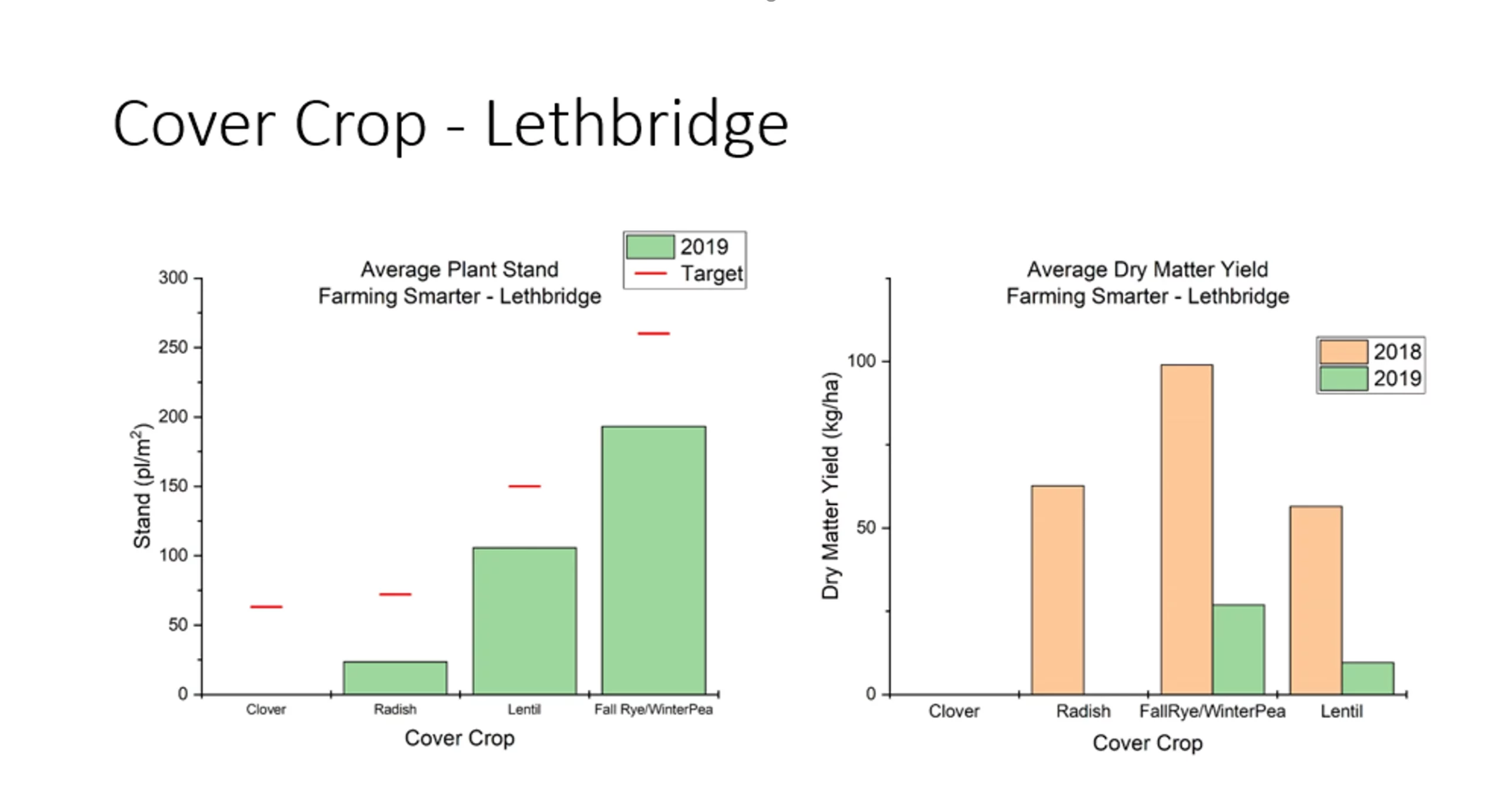
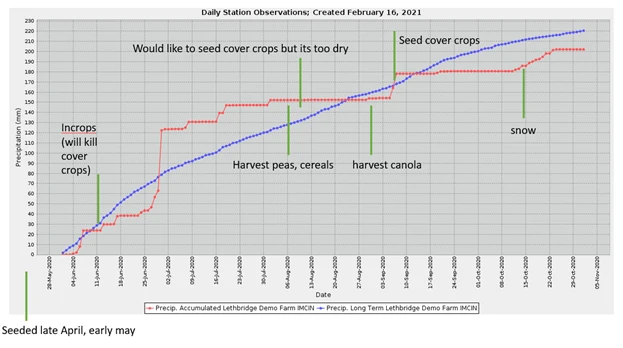
RecommendationsCover crops have proven difficult to grow in our rainfed prairie locations. Looking at figure 5, there are numerous potential times for planting a cover crop. One option is to plant both crops at seeding (intercropping), but in many cases our herbicides would terminate it. A second option would be to broadcast or knife in the cover crop seed after herbicide is applied. In most cases, we are too dry at that point for a new crop to establish. Our typical fall planting, the third option, is tough to harvest the previous crop and plant into good fall moisture for the cover crop. Our peas and cereals are typically harvested in early August, but we often have a month gap of lost growing season where conditions remain hot and dry. Under irrigation we could easily plant a new crop, but typically irrigation delays maturity and is reserved for higher value crops. In a dryland scenario, we must wait until fall conditions allow us to plant, which is typically early September. Our data (plant counts and biomass) indicates fall rye/winter pea and lentils are best adapted as cover crop. However, that poses the question why bother at all? If our most successful cover crops could just be fall seeded grain crops for the next year, maybe we need further research to compare cover crops and fall crops in drier areas?
Project Playlist
|
|||||||||
Articles
Use of cover crops has been increasing throughout the Prairies, but little is known about their benefits & detriments.
A Farming Smarter project is investigating how to incorporate cover crops in the fall season. Our strategy is to implement them within crop rotations.
This trial is a 4-year fully phased rotational trial (each year has each part of the rotation sequence) looking at the effect of cover crops on viability, yield and soil health.
Yvonne Lawley, University of Manitoba, talks about the goals of cover crop use on the prairies. Cover crops can improve soil, conserve water and strengthen a farmers bottom line.